A new episode of the Strawberry Chat podcast is available. In this episode, we talked with Dr. Marvin Pritts from Cornell University. We discussed the new edition of the Strawberry Production Guide for the Northeast, Midwest, and Eastern Canada. Dr. Marvin introduced us to the plasticulture day-neutral strawberry product system he has been researching recently.[Read More…]
2024 OISC Clean Sweep Pesticide Disposal WHAT: An OISC Clean Sweep Pesticide Disposal Program designed to collect and dispose of suspended, canceled, banned, unusable, opened, unopened or just unwanted pesticides (herbicides, insecticides, rodenticides, fungicides, miticides, etc.) is being sponsored by the Office of Indiana State Chemist (OISC). This disposal service is free of charge up[Read More…]
The Spotted Lanternfly is an invasive planthopper native to East Asia. It was introduced to the US in 2014 in Eastern Pennsylvania and has since spread to 13 other states including Indiana. The Spotted Lanternfly has 70+ host species including the invasive Tree of heaven (Alianthus altissma), grapes, apples, stone fruit, vegetables, hops, walnuts and[Read More…]
2023 OISC Clean Sweep Pesticide Disposal Information Form WHAT: An OISC Clean Sweep Pesticide Disposal Program designed to collect and dispose of suspended, canceled, banned, unusable, opened, unopened or just unwanted pesticides (herbicides, insecticides, rodenticides, fungicides, miticides, etc.) is being sponsored by the Office of Indiana State Chemist (OISC). This disposal service is free of[Read More…]
Tissue analysis is the most reliable means of determining plant nutritional status. Combined with soil testing, tissue analysis can help pinpoint the source of problems and determine what measures may be needed to ensure proper nutrition of the crop. Tissue analysis samples should be collected at the appropriate time to give the most meaningful results.[Read More…]
Shoot Thinning The optimum shoot density is 5-6 shoots per foot of row. Thinning to this density can help reduce shading, adjust the crop, lower the risk of disease and improve spray penetration. The optimal time for shoot thinning is before the shoots reach 12 inches. Much of the state is past this point, so[Read More…]
Shoots are at various stages of development across the state with some shoots at or near bloom. The most important time of the year for fruit disease control is from pre-bloom to 4-5 weeks past fruit set. The potential for fruit infection drops significantly 4-5 weeks post-bloom. Important diseases to control during this time include[Read More…]
Grapevines are in early stages of growth across the state. Significant shoot growth is expected with the warm weather predicted for this week. Disease Control This is a very important time to maintain preventative control over major grape diseases including Phomopsis, black rot, powdery mildew and downy mildew. Fungicide application should begin at 1-3 in[Read More…]
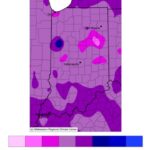
Grapevines are in various stages of early growth throughout Indiana, ranging from bud swell to 6-8 in shoot growth, depending on variety. A cold weather event came across the state on 4/24 bringing temperatures as low as 25°F (see Figure 1). The minimum temperatures in the following areas were reported as follows: Lafayette, IN: 28.9°F[Read More…]
Extreme cold temperatures were experienced across the state on December 23-24th 2022 (Figure 1). Temperatures ranged from -10- -5° F across most of the state with temperatures dipping below -10°F in some areas. Since then, there have been some additional cold events, such as 7° F on January 31-February 1 and 12° F on March[Read More…]